
Asked in Amazon
BST Iterator Problem Statement
You are tasked with creating a class named BSTIterator that acts as an iterator for the inorder traversal of a binary search tree. Implement the following functions:
BSTIterator(Node root): A constructor that inputs the root of the binary search tree and initializes the iterator.next(): Returns the next smallest element from the inorder traversal of the tree.hasNext(): Returnstrueif there remains a next element in the inorder traversal; otherwise, returnsfalse.
Assume the binary search tree contains 'N' nodes, and you must print its inorder traversal using the iterator.
Input:
The first line of the input includes an integer T representing the number of test cases.
Each test case consists of a single line with nodes in level order form, where -1 indicates a null node.
For example, the input corresponds to a tree: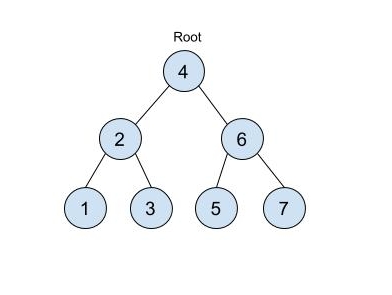
4
2 6
1 3 5 7
-1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1
Output:
Output for each test case should be a line containing the inorder traversal of the binary search tree.Example:
Input:
4 2 6 1 3 5 7 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1Output:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7Explanation:
Level 1:
The root node of the tree is 4
Level 2:
Left child of 4 = 2
Right child of 4 = 6
Level 3:
Left child of 2 = 1
Right child of 2 = 3
Left child of 6 = 5
Right child of 6 = 7
Level 4:
Each child node at this level is null (-1), and the input concludes with all null nodes.
The tree is traversed in inorder, hence the output is 1 2 3 4 5 6 7.Constraints:
- 1 <= T <= 10
- 1 <= N <= 104
- 1 <= A[i] <= 109
Note:
The input sequence is provided in a single line separated by spaces. Implementation of the given functions is sufficient as output is handled externally.
AnswerBot
4mo
Implement a BSTIterator class for inorder traversal of a binary search tree.
Create a BSTIterator class with constructor, next, and hasNext functions.
Use a stack to simulate inorder traversal of the bi...read more
Help your peers!


Add answer anonymously...
Top Software Developer Interview Questions Asked at Amazon
Q. Could you describe the process for designing a data structure that allows for al...read more
Q. What is Java?
Q. What is PHP?
Interview Questions Asked to Software Developer at Other Companies
Top Skill-Based Questions for Amazon Software Developer
Algorithms Interview Questions and Answers
250 Questions
Data Structures Interview Questions and Answers
250 Questions
Web Development Interview Questions and Answers
250 Questions
Java Interview Questions and Answers
250 Questions
SQL Interview Questions and Answers
250 Questions
Software Development Interview Questions and Answers
250 Questions
Stay ahead in your career. Get AmbitionBox app


Trusted by over 1.5 Crore job seekers to find their right fit company
80 L+
Reviews
10L+
Interviews
4 Cr+
Salaries
1.5 Cr+
Users
Contribute to help millions
AmbitionBox Awards
Get AmbitionBox app













