You are given a Binary Search Tree (BST) and a target value ‘K’. Your task is to check if there exist two unique elements in the given BST such that their sum is equal to the given target ‘K’.
A binary search tree (BST) is a binary tree data structure which has the following properties.
• The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with data less than the node’s data.
• The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with data greater than the node’s data.
• Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.
Note:
1. All the elements of the Binary Search Tree are unique.
2. You can’t use the same node value/element of BST twice.
Input Format:
The first line of input contains an integer ‘T’, which denotes the number of test cases. Then each test case follows.
The first line of every test case contains elements of Binary Search Tree in the level order form. The input consists of values of nodes separated by a single space in a single line. In case, a node is null, we take -1 in its place.
The second line of every test case contains a single integer ‘K’ which denotes the target value.
For example:
The input for the tree depicted in the below image would be :
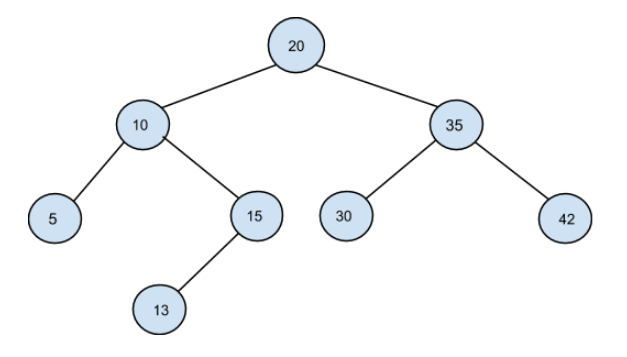
20 10 35 5 15 30 42 -1 13 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1
Explanation :
Level 1 :
The root node of the tree is 1
Level 2 :
Left child of 1 = 2
Right child of 1 = 3
Level 3 :
Left child of 2 = 4
Right child of 2 = null (-1)
Left child of 3 = 5
Right child of 3 = 6
Level 4 :
Left child of 4 = null (-1)
Right child of 4 = 7
Left child of 5 = null (-1)
Right child of 5 = null (-1)
Left child of 6 = null (-1)
Right child of 6 = null (-1)
Level 5 :
Left child of 7 = null (-1)
Right child of 7 = null (-1)
The first not-null node (of the previous level) is treated as the parent of the first two nodes of the current level. The second not-null node (of the previous level) is treated as the parent node for the next two nodes of the current level and so on.
The input ends when all nodes at the last level are null (-1).
Note:
The above format was just to provide clarity on how the input is formed for a given tree.
The sequence will be put together in a single line separated by a single space. Hence, for the above-depicted tree, the input will be given as:
1 2 3 4 -1 5 6 -1 7 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1
Output Format:
For each test case, print a single line containing “true” or “false”.
Note:
You don’t need to print the output, it has already been taken care of. Just implement the given function.
Constraints:
1 <= T <= 5
1 <= N <= 10 ^ 3
0 <= DATA <= 10 ^ 9
1 <= K <= 10 ^ 9
Where ‘DATA’ denotes the value of each node in the given tree and ‘N’ denotes the number of nodes in BST.
Time limit: 1 sec
This problem can be solved using hashing. The idea is to traverse the tree in an inorder fashion and insert every node’s value into a set. Also check if, for any node, the difference between the given...read more
The idea is that if the sum of any two elements say, ‘A’ and ‘B’ is equal to the given value ‘K’, and we already know that ‘A’ is present in the given tree then we only need to che...read more
In this approach, we use the property of the inorder traversal of BST. The inorder traversal of a BST always traverses the nodes of BST in the increasing order of their values.
Thus, ...read more
Instead of searching a second value for every node of the given BST, we can optimise our search by using a set to keep track of elements.
- We will traverse the tree in a depth-first-search ma...read more
In this approach, we will maintain a ‘FRONT’ and a ‘BACK’ iterator pointers that will iterate the BST in the order of in-order and reverse in-order traversal respectively.
Approa...read more
Top VMware Software Software Developer interview questions & answers
Popular interview questions of Software Developer

Reviews
Interviews
Salaries
Users/Month