Add office photos
Employer?
Claim Account for FREE
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
4.0
based on 3 Reviews
About University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
Founded in1970 (55 yrs old)
India Employee Count--
Global Employee Count501-1k
HeadquartersChampaign, United States
Office Locations
--
Websiteuiuc.edu
Primary Industry
Other Industries
--
Are you managing University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign's employer brand? To edit company information,
claim this page for free
Managing your company's employer brand?
Claim this Company Page for FREE
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Ratings
based on 3 reviews
Overall Rating
4.0/5
How AmbitionBox ratings work?
5
0
4
3
3
0
2
0
1
0
Category Ratings
4.3
Work-life balance
4.2
Skill development
3.9
Company culture
3.9
Work satisfaction
3.7
Job security
2.3
Promotions
2.0
Salary
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign is rated 4.0 out of 5 stars on AmbitionBox, based on 3 company reviews. This rating reflects a generally positive employee experience, indicating satisfaction with the company’s work culture, benefits, and career growth opportunities. AmbitionBox gathers authentic employee reviews and ratings, making it a trusted platform for job seekers and employees in India.
Read more
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Reviews
Compare University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign with Similar Companies
Change Company | Change Company | Change Company | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Overall Rating | 4.0/5 based on 3 reviews | 3.6/5 based on 1.2k reviews | 3.4/5 based on 3.3k reviews | 3.9/5 based on 1.5k reviews |
Highly Rated for | Work-life balance Skill development Company culture | Job security | No highly rated category | Skill development Work-life balance Salary |
Critically Rated for | Salary Promotions | Promotions Skill development Salary | Work-life balance Promotions Job security | No critically rated category |
Primary Work Policy | - | Work from office 98% employees reported | Work from office 87% employees reported | Work from office 95% employees reported |
Rating by Women Employees | - no rating available | 3.4 Average rated by 423 women | 3.4 Average rated by 933 women | 3.9 Good rated by 775 women |
Rating by Men Employees | - no rating available | 3.8 Good rated by 652 men | 3.4 Average rated by 2.2k men | 3.9 Good rated by 576 men |
Job security | 3.7 Good | 3.8 Good | 3.1 Average | 3.7 Good |
View more
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Salaries
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign salaries have received with an average score of 2.0 out of 5 by 3 employees.
Teaching Assistant
(2 salaries)
Unlock
₹4.7 L/yr - ₹6 L/yr
Research Assistant
(2 salaries)
Unlock
₹15.8 L/yr - ₹20.1 L/yr
Graduate Research Assistant
(2 salaries)
Unlock
₹14.9 L/yr - ₹19 L/yr
Postdoctoral Research Associate
(2 salaries)
Unlock
₹2.7 L/yr - ₹3.5 L/yr
Research Technician
(2 salaries)
Unlock
₹36 L/yr - ₹46 L/yr
Data Scientist
(1 salaries)
Unlock
₹96 L/yr - ₹1.1 Cr/yr
Assistant Professor
(1 salaries)
Unlock
₹16.2 L/yr - ₹20.7 L/yr
Program Manager
(1 salaries)
Unlock
₹13.5 L/yr - ₹17.2 L/yr
Software Engineer
(1 salaries)
Unlock
₹9.9 L/yr - ₹12.7 L/yr
Research Analyst
(1 salaries)
Unlock
₹21.6 L/yr - ₹27.6 L/yr
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign News
View all
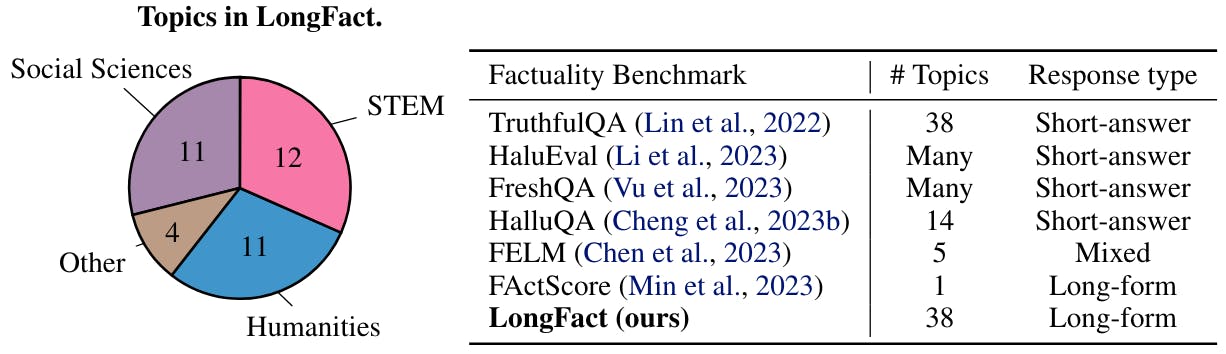
How LongFact Helps AI Models Improve Their Accuracy Across Multiple Topics
- LongFact is a prompt set designed to examine factuality in long-form responses.
- LongFact consists of two tasks, LongFact-Concepts and LongFact-Objects.
- LongFact is publicly available at http://nauk.in/y7gE3gjS
- The authors involved in the research are from Google DeepMind, Stanford University, and the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign.
Hackernoon | 9 Apr, 2025
SAFE: A New AI Tool for Fact-Checking Long-Form Responses
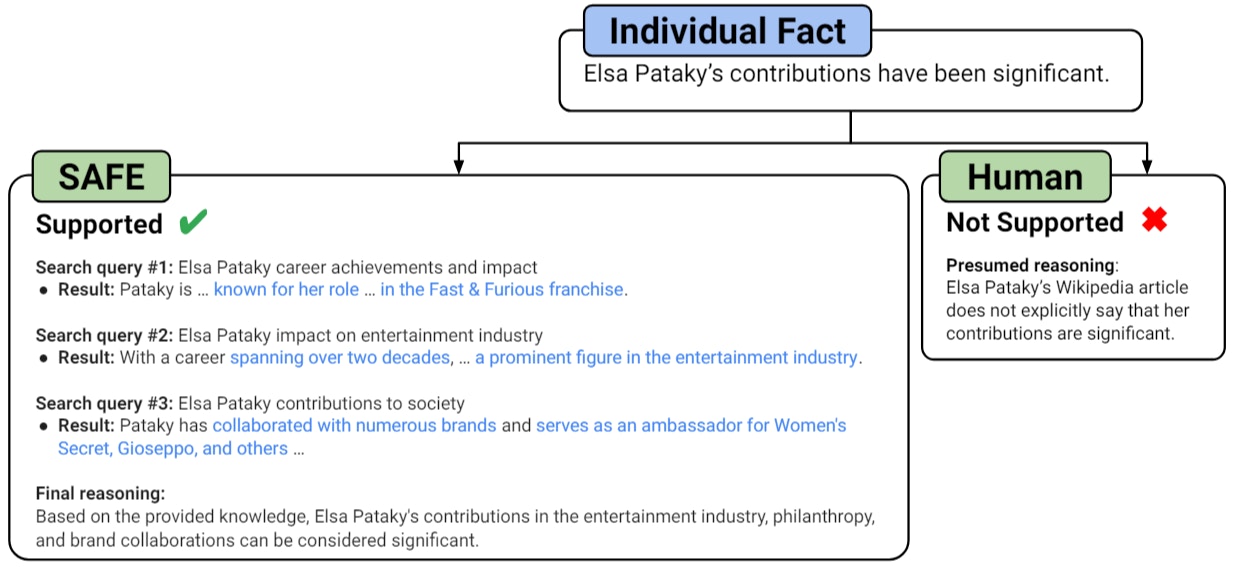
- Existing automated evaluation methods like BLEURT, ROUGE, and prompting language models are not optimal for long-form responses as they lack comprehensive reference answers.
- Proposed SAFE tool evaluates long-form factuality by splitting responses into individual facts and using Google Search for dynamic reference answers.
- SAFE uses a language model to determine relevance of each fact, issue multi-step Google Search queries, and assess support for the facts in the search results.
- The key innovation in SAFE is employing a language model to generate Google Search queries and reason about fact support.
- To rate self-contained facts, the model assesses relevance to the prompt and determines whether they are supported or not supported by search results.
- SAFE's output metrics include the number of supported, irrelevant, and not-supported facts in a prompt-response pair.
- The paper is available on arxiv under CC by 4.0 Deed license and authors include contributors from Google DeepMind and other institutions.
- SAFE draws inspiration from prior works and aims to enhance the evaluation of long-form factuality.
- The tool's detailed implementation and code are publicly accessible on GitHub under a specific repository.
- Authorship of the paper includes several individuals from Google DeepMind, Stanford University, and the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign.
Hackernoon | 9 Apr, 2025
Why LLMs Are More Accurate and Cost-Effective Than Human Fact-Checkers
- LLMs have demonstrated superior performance on reasoning benchmarks and higher factuality than humans on summarization tasks.
- The prevalent use of human annotators in language-model research results in high costs and variations in evaluation speed and quality.
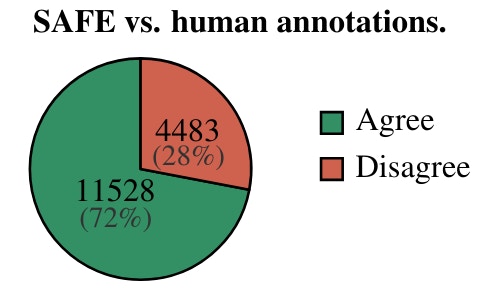
- The study investigates how SAFE compares to human annotations and its potential to replace human raters in evaluating long-form factuality.
- By leveraging crowdsourced human annotations, SAFE achieved a 72.0% agreement with humans on individual facts.
- In cases of disagreement, SAFE annotations were found to be correct 76% of the time compared to human annotations at 19%.
- SAFE is not only more accurate but also more cost-effective, costing $0.19 per model response compared to $4 per model response with human annotators.
- The study proposes F1@K as a metric combining factual precision and recall, allowing standardized comparisons between language models.
- F1@K measures the long-form factuality of a model response based on the number of supported and not-supported facts in the response.
- The authors of the study include individuals from Google DeepMind, Stanford University, and the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign.
Hackernoon | 9 Apr, 2025
ChatGPT Earns High Marks for Food Analysis Expertise
- Artificial intelligence (AI) is making waves in sensory evaluation, particularly in food science, as demonstrated in a study on brownies by the University of Illinois.
- The study aimed to streamline sensory evaluation processes that are traditionally resource-intensive and time-consuming by leveraging AI, specifically ChatGPT.
- ChatGPT was utilized to predict sensory attributes of fifteen brownie recipes, showcasing positive evaluations despite unconventional ingredients.
- The study highlighted ChatGPT's bias towards positive evaluations due to training on optimistic language datasets, pointing to the need for bias correction in AI models.
- AI like ChatGPT could serve as a valuable screening tool in food product development, optimizing resource allocation and enhancing innovation cycles.
- While AI shows promise in assisting with initial product quality assessments, efforts are needed to refine AI's perceptual accuracy to align with human sensory experiences.
- The study suggests a future where AI, through improved descriptive vocabulary training, becomes an integral part of sensory evaluation in food product development.
- This research hints at broader implications for AI integration in food science, potentially leading to more diverse and innovative food product lines.
- While AI may not replace human testers in sensory evaluation yet, the study underscores AI's potential in enhancing product development and innovation within the food industry.
- The findings open avenues for further research to refine AI systems and establish their calibration for more sophisticated applications in sensory evaluation.
Bioengineer | 29 Mar, 2025

Beyond RAG: SEARCH-R1 integrates search engines directly into reasoning models
- The ability of Large Language Models (LLMs) to incorporate external data in reasoning has been limited.
- SEARCH-R1, introduced by researchers from University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign and University of Massachusetts Amherst, integrates search engines into LLMs for reasoning.
- SEARCH-R1 allows LLMs to generate search queries and use search engine results seamlessly during reasoning tasks.
- By incorporating up-to-date data from search engines, SEARCH-R1 enhances LLMs' reasoning capabilities with external knowledge.
- RAG and prompting-based tool use have limitations for integrating search engines with LLMs in reasoning models.
- SEARCH-R1 enables LLMs to interact with search engines within the reasoning process, improving multi-turn, multi-query retrieval.
- The researchers applied pure reinforcement learning in training SEARCH-R1 to streamline the model's integration of reasoning and search tools.
- SEARCH-R1 outperforms baseline methods, showcasing the effectiveness of incorporating search retrieval in LLM reasoning tasks.
- The code for SEARCH-R1 has been made available on GitHub, demonstrating its applicability in different model families for enhanced decision-making.
- SEARCH-R1's autonomous generation of search queries and real-time data integration can benefit enterprise applications like customer support and data analysis.
VentureBeat | 19 Mar, 2025

HippoRAG 2: Advancing Long-Term Memory and Contextual Retrieval in Large Language Models
- HippoRAG 2 is a neurobiologically inspired long-term memory framework for LLMs, enhancing the original HippoRAG by improving context integration and retrieval.
- HippoRAG 2, developed by researchers from The Ohio State University and the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, improves factual recall, sense-making, and associative memory in large language models.
- HippoRAG 2 achieves a 7% improvement in associative memory tasks over leading embedding models while maintaining strong factual and contextual understanding.
- HippoRAG 2 significantly advances non-parametric continual learning, bringing AI systems closer to human-like long-term memory capabilities.
Marktechpost | 4 Mar, 2025
Scientists Innovate Advanced Technique for Monitoring Antibiotic Resistance in Wastewater
- Researchers from the Carl R. Woese Institute for Genomic Biology have developed a CRISPR-enriched metagenomics approach to enhance the detection of antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) in wastewater, addressing the global health challenge of antibiotic resistance.
- The study aims to improve surveillance methods for tracking the emergence and spread of over 5,000 distinct ARGs found in various ecosystems, including hospitals, agricultural runoffs, and sewage systems.
- By incorporating the CRISPR-Cas9 system, the researchers achieved a significant improvement in the efficiency of detecting ARGs, resulting in the identification of 1,189 additional ARGs in wastewater samples.
- This innovative method enriched the detection limit of ARGs from 10^-4 to 10^-5, showcasing its potential for revolutionizing public health strategies and interventions in combating antibiotic resistance.
- The research team, led by graduate student Yuqing Mao and Professor Helen Nguyen, plans to further develop their CRISPR-enriched metagenomic method for broader environmental applications, supported by funding from various organizations.
- The integration of advanced techniques like CRISPR technology is crucial in staying ahead of the antibiotic resistance crisis and preparing for future health implications associated with resistant bacterial strains.
- Through collaborative efforts and innovative research approaches, the global response to antibiotic resistance can become more proactive and informed, contributing to a safer environment for all.
- The research into CRISPR-enriched metagenomics method signifies a significant advancement in monitoring antibiotic resistance genes, emphasizing the importance of swift and efficient detection methods in combating this pressing issue.
- This study not only offers a blueprint for future research but also highlights the potential benefits of integrating cutting-edge genetic engineering techniques into environmental monitoring frameworks for public health protection.
- By leveraging advanced methodologies such as CRISPR-enriched metagenomics, researchers are bridging the gap between discovery and application, contributing to a proactive approach in the battle against antibiotic resistance.
- The groundbreaking work at the University of Illinois underscores the importance of continuous innovation and collaboration in addressing the challenges posed by antibiotic resistance, signaling a new era in the fight against resistant bacterial strains.
Bioengineer | 4 Mar, 2025

Illinois Researchers Unveil Advanced Organic Nanozymes and Innovative Point-of-Use System for Agricultural and Food Applications
- University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign researchers have developed advanced organic nanozymes that mimic enzyme catalytic properties, offering non-toxic, sustainable, and cost-effective alternatives for agricultural and food applications.
- These organic nanozymes overcome the limitations of traditional inorganic nanozymes by utilizing essential amino acid L-alanine and polyethylene glycol to enhance structural integrity and catalytic activities.
- The nanozymes, reduced to less than 100 nanometers in size, have showcased potential for real-world use, particularly in agricultural practices and food safety protocols.
- Integration with a colorimetric sensing platform has enabled the detection of histamine in food products, addressing health risks associated with high histamine levels in vegetables like spinach and eggplant.
- The innovative sensing platform, designed for point-of-use applications, simplifies the detection of substances like glyphosate, while smartphone technology enhances user experience in rapid molecule detection.
- This advancement marks a significant shift towards sustainable agricultural practices and eco-friendly food production methods, emphasizing the global focus on environmental health and food security.
- The research at the University of Illinois demonstrates a proactive approach to enhancing food safety and agricultural efficiency through the development of organic nanozymes and integrated sensing technologies.
- The intersection of durable, biodegradable materials with innovative sensing platforms signifies a commitment to effective solutions with minimal ecological impact, paving the way for transformative applications in various fields.
- These breakthroughs not only offer alternatives to conventional methods but also present a model for future research initiatives, shaping the trajectory of food safety and agricultural practices.
- The potential widespread adoption of organic nanozymes could revolutionize the landscape of food safety and agriculture, culminating in sustainable and efficient practices for future generations.
- Continued innovation in organic nanozymes and sensing technologies promises further advancements crucial for ensuring accessible, efficient, and sustainable food safety measures in the future.
Bioengineer | 1 Mar, 2025

DARPA Wants to Build Structures in Orbit, Without Needing a Launch from Earth
- DARPA is partnering with universities to develop 3D printing technology and in-orbit assembly of satellite components.
- DARPA's NOM4D program aims to send lightweight materials to space for on-site construction, enabling the building of larger and more mass-efficient structures in orbit.
- Partnerships with Caltech and the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign are progressing to in-space testing of the assembly process for smaller satellites.
- DARPA is exploring the possibility of growing large biological structures in space to enable new construction possibilities.
Universe Today | 28 Feb, 2025

DARPA begins testing phase for in-orbit space construction
- DARPA's NOM4D program has transitioned to small-scale orbital demonstrations to evaluate materials and assembly techniques for large-scale orbital structures.
- Caltech and Momentus will demonstrate autonomous robotic assembly technology to construct a circular truss in space.
- The University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign will showcase a high-precision in-space composite-forming process on the International Space Station.
- The success of these demonstrations could lead to the construction of large-scale space infrastructure and an in-space manufacturing ecosystem.
TechSpot | 14 Feb, 2025

Powered by
Compare University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign with

Chandigarh University
4.1

Podar International School
4.2

Orchids International School
3.0

Sri Chaitanya Educational Institutions
3.8

ALLEN Career Institute
3.9

CADD Centre Training Services
3.9

uFaber
2.5

DAV Public School
4.0

Lovely Professional University
3.4

ICA Edu Skills
4.0

Mount Litera Zee School
3.9

Centum Learning
3.8

Narayana e-Techno School
3.7

St. Xavier's High School
3.9

GD Goenka Public School
3.4

Eurokids
4.1

Pearson Education India
3.9

ICFAI University
3.6

Pratham Education Foundation
4.1

Triumphant Institute of Management Education
3.7
Edit your company information by claiming this page
Contribute & help others!
You can choose to be anonymous
Companies Similar to University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign

Aakash Educational Services
Education & Training
3.4
• 3.3k reviews

Frankfinn Institute of Air Hostess Training
Education & Training
3.9
• 1.5k reviews

Amity University
Education & Training
3.6
• 1.2k reviews

Chandigarh University
Education & Training
4.1
• 1.1k reviews

Podar International School
Education & Training
4.2
• 948 reviews

Orchids International School
Education & Training
3.0
• 955 reviews

Sri Chaitanya Educational Institutions
Education & Training
3.8
• 899 reviews

ALLEN Career Institute
Education & Training
3.9
• 744 reviews

CADD Centre Training Services
Education & Training
3.9
• 711 reviews

uFaber
Internet, Education & Training
2.5
• 656 reviews

DAV Public School
Education & Training
4.0
• 613 reviews

Lovely Professional University
Education & Training
3.4
• 603 reviews
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign FAQs
When was University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign founded?
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign was founded in 1970. The company has been operating for 55 years primarily in the Education & Training sector.
Where is the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign headquarters located?
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign is headquartered in Champaign.
What are the pros and cons of working in University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign?
Working at University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign comes with several advantages and disadvantages. It is highly rated for work life balance, skill development and company culture. However, it is poorly rated for salary & benefits and promotions / appraisal, based on 3 employee reviews on AmbitionBox.
Stay ahead in your career. Get AmbitionBox app

Helping over 1 Crore job seekers every month in choosing their right fit company
75 Lakh+
Reviews
5 Lakh+
Interviews
4 Crore+
Salaries
1 Cr+
Users/Month
Contribute to help millions
Get AmbitionBox app